
- Moisture
- Commercial
- Blog
Durable Design: Using Technology to Achieve Expected Building Service Lifespans
Blog in Brief
Multiple building science elements must be considered when establishing the design for a building, including moisture and heat transfer, building material performance and the intended lifespan of the building. Using modeling technology like Fraunhofer IBP’s WUFI® to understand the fundamentals that influence longevity and building material behavior and interaction. Design plans and material choices can be tailored to deliver the intended lifespan of the building.
Durable Design: Using Technology to Achieve Expected Building Service Lifespans
One element of building science that is generating excitement is work on design durability. Using new technology and improved analysis of materials, heat and moisture, we can help architects and designers tailor plans to provide specified building service lifespans.
Our hygrothermal experts aim to help industry members understand the physics of moisture and heat transfer, as green building projects and zero-energy buildings emphasize the role of insulation and airtight enclosures.
Service life and durable designs
Although there are different ways of assessing building plans, using the lens of design durability helps architects or designers better match plans with the anticipated or desired building lifespan prior to specification. For example, plans for strip malls, which can be designed to require renovation about every 15 years, may make different decisions or call for using different materials compared to plans for a building intended to have a 50- to 100-year lifespan.
Designs need to match the intention behind the building. Making a durability assessment can help ensure that the two elements – the design and practical implementation – correspond.
The durability assessment considers several factors, including balances of moisture, heat and air flow within the building and that materials used to ensure the design match the planned service life.
An initial step in the durable design process determines inside load and outside load. When considering the moisture load, it’s important to remember that there tends to be a difference in vapor pressure between outdoor and indoor spaces, and to account for moisture movement through structural elements like a building’s envelope.
The data points gathered from the initial step are then examined on the basis of heat, air and moisture transport. This information supports a durability analysis, which considers the value of individual design elements as they relate to the anticipated moisture pressure and movement of heat, air and water. Understanding the interactions between elements like moisture load or air flow load can be used to help determine how long materials will provide constant performance.
A final step in the durable design process is what helps separate our system and practices from other industry practices. Once the moisture and airflow data has been collected and analyzed, that information is reviewed based on an understanding of what it means for durability and the performance of the building’s envelope.
Using the collected data and analysis from the durable design process helps support material-related predictions such as estimating the onset of corrosion for a steel stud wall system and generating alternative options based on intended lifespan. The predictions and inclusion of alternatives could also be used to more finely tailor other elements involved, including project service life.
Technology and durable design assessments
One tool that helps inform and generate the analyses used in durable design work is the WUFI® – or Wärme Und Feuchte Instationär group of software programs. WUFI® was created by Hartwig Künzel, head of the Hygrothermics Department at Fraunhofer IBP, and Achilles Karagiozis, director of NREL’s Buildings and Thermal Sciences Center, and is maintained by a team in the Hygrothermics Department at the Fraunhofer Institute for Building Physics (IBP). The system can be used to develop realistic hygrothermal analysis or, to put it another way, to assess coupled heat and moisture transfer through multi-layer materials, buildings and component connections using simulated real-world conditions.
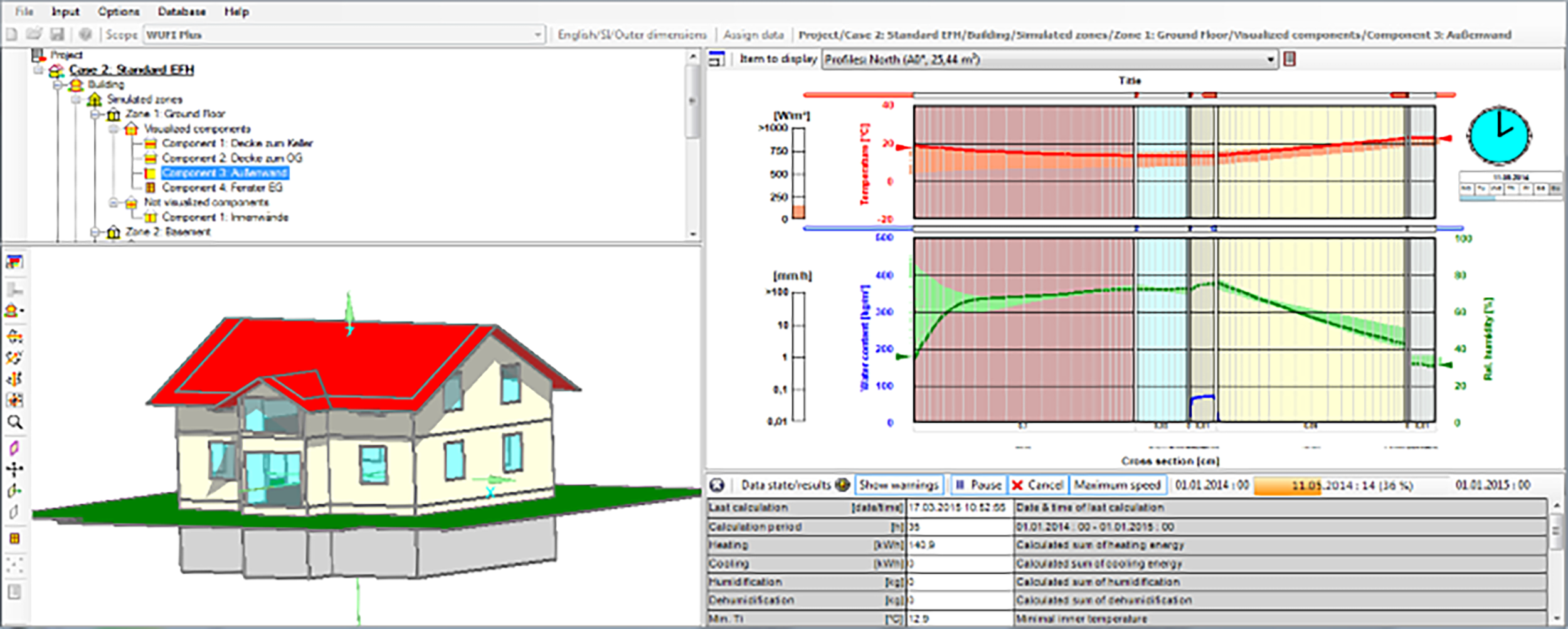
This consideration helps predict moisture balance, air flow balance and energy balance for a design, creating a dynamic understanding of how heat, air and moisture move. This dynamic understanding can then be used as the basis for estimations made about the start of durability changes and help predict service life for a specific building. In other words, a better grasp of heat, air and moisture transport informs the predictions used to refine the review of a design’s durability and service life.
Conclusion
At Owens Corning, we have long studied and relied on building science to support the design process and help architects find the needed solutions for every project. One element of our research in this area has been to develop our understanding and expertise regarding work with durable designs. This effort focused on using knowledge of heat, moisture and air flow to refine durability predictions for a building’s envelope to better match the insulation layer recommendations with elevated building service lifespans.
Related Articles
Related Articles

Fire • Commercial • BlogMineral Wool Wall Insulation & Fire Safety

Fire • Commercial • BlogStone Wool Versus Slag Wool Insulation

Moisture • Commercial • Blog7 Key Factors for Selecting Commercial Roof Insulation

Fire • Industrial • WebinarLNG Pool Fire Suppression & Cryogenic Liquid Spill Protection

Fire • Commercial • BlogThermafiber®, the Workhorse in Perimeter Fire Containment, Celebrates 90 Years

Fire • Commercial • BlogFAQs About Thermafiber® Mineral Wool Insulation

Fire • Industrial • BlogCombustible Liquids in Insulation

Fire • Industrial • BlogThe Behavior of Industrial Insulation in Case of Fire

Moisture • Industrial • BlogSpecifying Insulation to Support Longevity in Chilled Water Systems

Fire • Industrial • WebinarPassive Fire Protection Systems Webinar

Moisture • Industrial • WebinarChilled Water Systems Webinar

Fire • Industrial • BlogMitigating LNG pool fires using passive systems

Fire • Industrial • BlogFire testing takeaways to consider when selecting insulation for fire protection

Fire • Commercial • BlogBalancing life safety, installation efficiency and design flexibility

Moisture • Industrial • BlogDesigning chilled water insulation systems to mitigate regional conditions

Moisture • Industrial • BlogUsing Cellular Glass Insulation to Mitigate Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI)

Moisture • Commercial • BlogVersatile VRAs: The role of XPS in VRA function and design

Moisture • Commercial • BlogOpinions and opportunities in building for resilience

Moisture • Mechanical • BlogDesign considerations for district energy insulation systems

Moisture • Industrial • BlogConsiderations for insulating district energy systems

Fire • Commercial • BlogNavigating Six Special Conditions in Perimeter Fire Containment System Design

Moisture • Commercial • Blog3 Benefits of Mineral Wool Continuous Insulation (ci) for Moisture Management

Fire • Commercial • BlogDismantling 5 Common Perimeter Fire Containment Misconceptions

Moisture • Mechanical • BlogFive mechanical insulation considerations for healthcare facilities

Fire • Mechanical • BlogProtecting life safety in plenum spaces

Moisture • Commercial • BlogUsing WUFI® as a moisture management design tool

Fire • Commercial • Blog3 Components of Fire Protection for Balanced Life Safety

Fire • Commercial • BlogSix Critical Components of a Listed Perimeter Fire Containment Assembly

Moisture • Commercial • BlogDurable Design: Using Technology to Achieve Expected Building Service Lifespans

Fire • Commercial • BlogUnderstanding the SAFETY Act: Using perimeter fire containment systems to reduce liability

Fire • Commercial • BlogSix Critical Components of Engineering Judgments for PFC Systems
Jump to a Solution Suite
Jump to a Solution Suite




